Cómo instalar el servidor multimedia Jellyfin en Debian 10
Jellyfin es un sistema de streaming multimedia de código abierto que te permite gestionar y transmitir tus medios. Es multiplataforma y alternativo a otras aplicaciones como Emby y Plex. Con Jellyfin, puedes organizar y compartir tus archivos multimedia, programas de TV, música y fotos desde la interfaz basada en la web. Puedes acceder a esos medios transmitidos en tu PC, tableta, teléfono, Roku y TV a través de Internet. Jellyfin obtiene automáticamente los metadatos de las bases de datos TheMovieDB, OpenMovie, Rotten Tomatoes y TheTVDB.
En este post, te mostraremos cómo instalar el servidor de streaming multimedia Jellyfin con Nginx como proxy inverso en Debian 10.
Requisitos previos
- Un servidor con Debian 10.
- Un nombre de dominio válido apuntado con la IP de tu servidor.
- Una contraseña de root configurada el servidor.
Cómo empezar
En primer lugar, tendrás que actualizar los paquetes de tu sistema con la última versión. Puedes actualizarlos con el siguiente comando:
apt-get update -y
Una vez actualizados todos los paquetes, instala otros paquetes necesarios con el siguiente comando:
apt-get install apt-transport-https ca-certificates gnupg2 curl git -y
Una vez instalados todos los paquetes, puedes pasar al siguiente paso.
Instalar Jellyfin
Por defecto, el paquete Jellyfin no está incluido en el repositorio de Debian 10. Así que tendrás que añadir el repositorio de Jellyfin a tu APT.
Puedes añadirlo con el siguiente comando:
echo "deb [arch=$( dpkg --print-architecture )] https://repo.jellyfin.org/debian buster main" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jellyfin.list
Una vez añadido el repositorio, añade la clave GPG con el siguiente comando:
wget -O - https://repo.jellyfin.org/jellyfin_team.gpg.key | apt-key add -
A continuación, actualiza el repositorio e instala Jellyfin con el siguiente comando:
apt-get update -y
apt-get install jellyfin -y
Una vez instalado Jellyfin, puedes comprobar el estado de Jellyfin con el siguiente comando:
systemctl status jellyfin
Deberías obtener la siguiente salida:
? jellyfin.service - Jellyfin Media Server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/jellyfin.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Drop-In: /etc/systemd/system/jellyfin.service.d
??jellyfin.service.conf
Active: active (running) since Mon 2021-03-22 08:27:42 UTC; 5min ago
Main PID: 10192 (jellyfin)
Tasks: 17 (limit: 4701)
Memory: 113.9M
CGroup: /system.slice/jellyfin.service
??10192 /usr/bin/jellyfin --webdir=/usr/share/jellyfin/web --restartpath=/usr/lib/jellyfin/restart.sh --ffmpeg=/usr/lib/jellyfin-ffm
Mar 22 08:27:45 debian10 jellyfin[10192]: [08:27:45] [WRN] 127.0.0.1/32: GetBindInterface: Loopback 127.0.0.1 returned.
Mar 22 08:27:45 debian10 jellyfin[10192]: [08:27:45] [INF] Executed all pre-startup entry points in 0:00:00.1545678
Mar 22 08:27:45 debian10 jellyfin[10192]: [08:27:45] [INF] Core startup complete
Mar 22 08:27:46 debian10 jellyfin[10192]: [08:27:46] [INF] Executed all post-startup entry points in 0:00:00.1976994
Mar 22 08:27:46 debian10 jellyfin[10192]: [08:27:46] [INF] Startup complete 0:00:03.6985068
Mar 22 08:27:48 debian10 jellyfin[10192]: [08:27:48] [INF] StartupTrigger fired for task: Update Plugins
Mar 22 08:27:48 debian10 jellyfin[10192]: [08:27:48] [INF] Queuing task PluginUpdateTask
Mar 22 08:27:48 debian10 jellyfin[10192]: [08:27:48] [INF] Executing Update Plugins
Mar 22 08:27:49 debian10 jellyfin[10192]: [08:27:49] [INF] Update Plugins Completed after 0 minute(s) and 0 seconds
Mar 22 08:27:49 debian10 jellyfin[10192]: [08:27:49] [INF] ExecuteQueuedTasks
En este momento, Jellyfin está iniciado y escuchando en el puerto 8096. Puedes comprobarlo con el siguiente comando:
ss -antpl | grep 8096
Salida:
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:8096 0.0.0.0:* users:(("jellyfin",pid=10192,fd=289))
Configurar Nginx como proxy inverso
A continuación, tendrás que configurar Nginx como proxy inverso para acceder a Jellyfin en el puerto 80.
Primero, instala el paquete Nginx con el siguiente comando:
apt-get install nginx -y
Una vez instalado, crea un nuevo archivo de configuración de Nginx con el siguiente comando:
nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/jellyfin.conf
Añade las siguientes líneas:
server {
listen 80;
server_name jellyfin.example.com;
access_log /var/log/nginx/jellyfin.access;
error_log /var/log/nginx/jellyfin.error;
set $jellyfin 127.0.0.1;
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8096;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Protocol $scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $http_host;
# Disable buffering when the nginx proxy gets very resource heavy upon streaming
proxy_buffering off;
}
# location block for /web - This is purely for aesthetics so /web/#!/ works instead of having to go to /web/index.html/#!/
location ~ ^/web/$ {
# Proxy main Jellyfin traffic
proxy_pass http://$jellyfin:8096/web/index.html/;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Protocol $scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $http_host;
}
location /socket {
# Proxy Jellyfin Websockets traffic
proxy_pass http://$127.0.0.1:8096;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Protocol $scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $http_host;
}
# Security / XSS Mitigation Headers
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN";
add_header X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block";
add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff";
}
Guarda y cierra el archivo y luego verifica que Nginx no tenga ningún error de sintaxis con el siguiente comando
nginx -t
Salida:
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
A continuación, reinicia el servicio Nginx para aplicar los cambios:
systemctl reload nginx
Accede a Jellyfin
Ahora, abre tu navegador web y accede a la interfaz web de Jellyfin utilizando la URL http://jellyfin.example.com. Serás redirigido a la siguiente página:
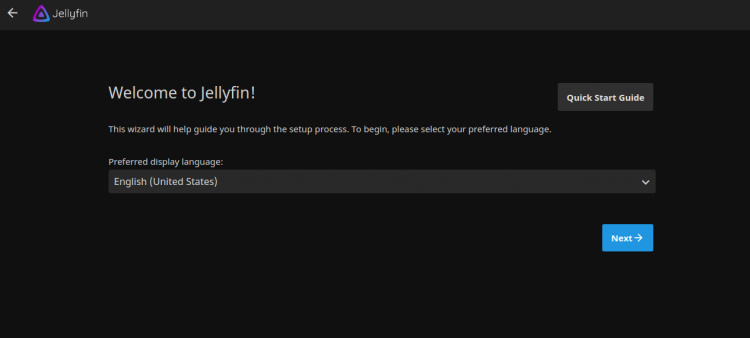
Selecciona tu idioma y haz clic en el botón Siguiente. Deberías ver la siguiente página:
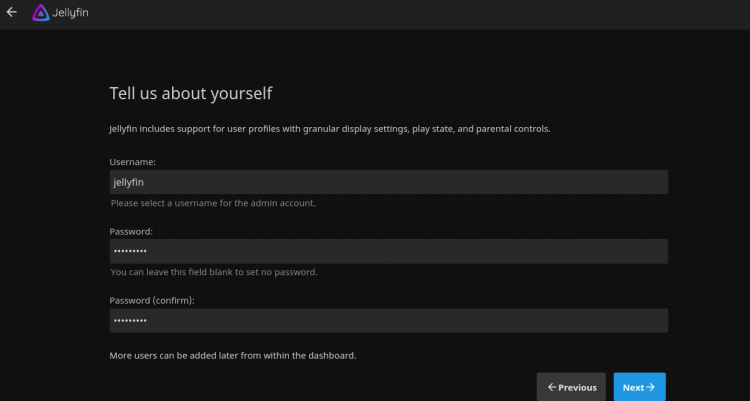
Proporciona tu nombre de usuario, contraseña y haz clic en el botón Siguiente. Deberías ver la siguiente página:
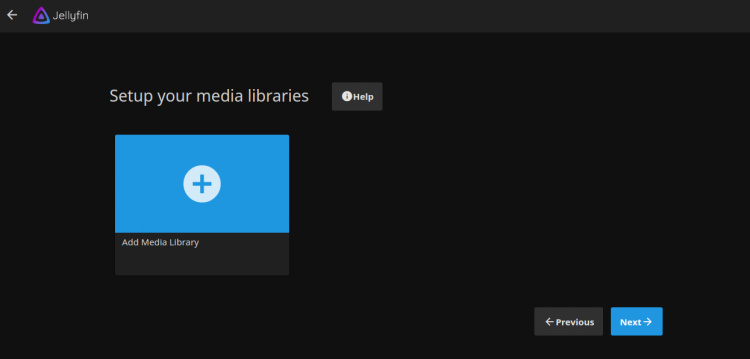
Haz clic en el botón Siguiente. Deberías ver la siguiente página:
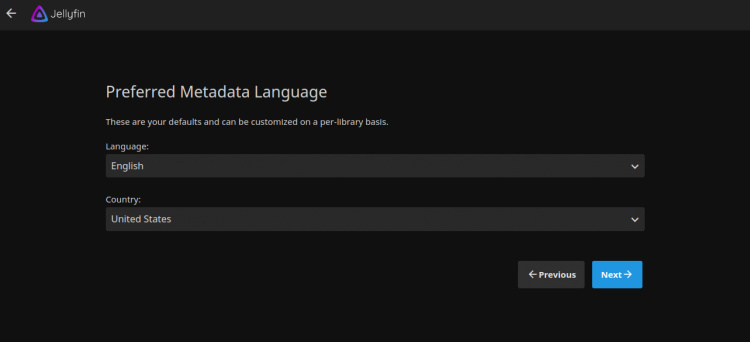
Selecciona el idioma de tus metadatos y haz clic en el botón Siguiente. Deberías ver la siguiente página:
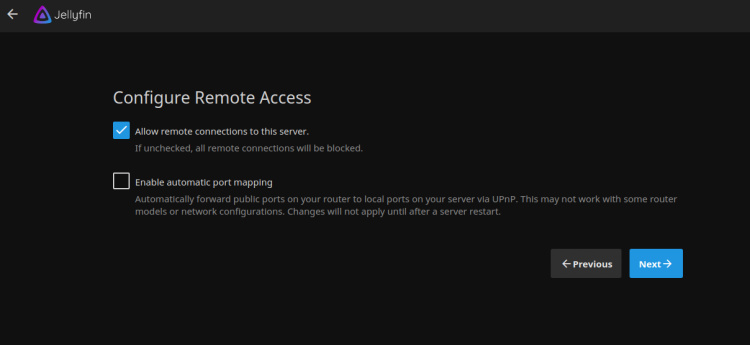
Permitir el acceso remoto y hacer clic en el botón Siguiente. Una vez finalizada la instalación, deberías ver la siguiente página:
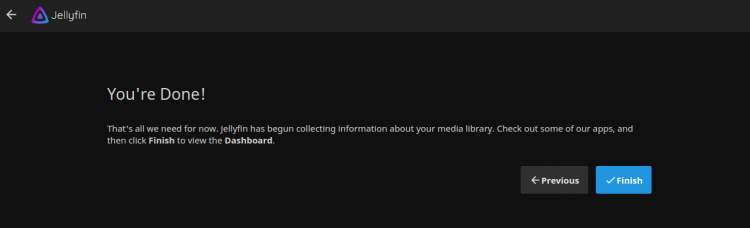
Haz clic en el botón Finalizar para terminar la instalación. Deberías ver la página de inicio de sesión de Jellyfin:
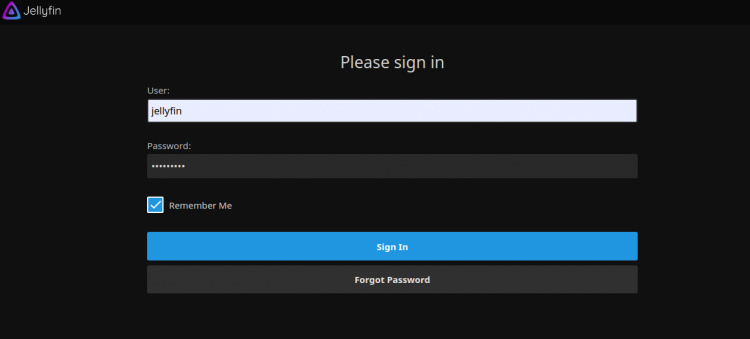
Proporciona tu nombre de usuario, tu contraseña y haz clic en el botón Iniciar sesión. Deberías ver el panel de control de Jellyfin en la siguiente página:
Asegura Jellyfin con Let’s Encrypt SSL
A continuación, tendrás que instalar el paquete cliente Certbot para instalar y gestionar el SSL de Let’s Encrypt. Primero, instala el Certbot con el siguiente comando:
apt-get install python3-certbot-nginx -y
Una vez terminada la instalación, ejecuta el siguiente comando para instalar el SSL de Let’s Encrypt en tu sitio web:
certbot --nginx -d jellyfin.example.com
Se te pedirá que proporciones una dirección de correo electrónico válida y que aceptes las condiciones del servicio, como se muestra a continuación:
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log Plugins selected: Authenticator nginx, Installer nginx Enter email address (used for urgent renewal and security notices) (Enter 'c' to cancel): [email protected] - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Please read the Terms of Service at https://letsencrypt.org/documents/LE-SA-v1.2-November-15-2017.pdf. You must agree in order to register with the ACME server at https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (A)gree/(C)ancel: A - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Would you be willing to share your email address with the Electronic Frontier Foundation, a founding partner of the Let's Encrypt project and the non-profit organization that develops Certbot? We'd like to send you email about our work encrypting the web, EFF news, campaigns, and ways to support digital freedom. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (Y)es/(N)o: Y Obtaining a new certificate Performing the following challenges: http-01 challenge for jellyfin.example.com Waiting for verification... Cleaning up challenges Deploying Certificate to VirtualHost /etc/nginx/conf.d/jellyfin.conf
A continuación, elige si quieres redirigir el tráfico HTTP a HTTPS como se muestra a continuación:
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1: No redirect - Make no further changes to the webserver configuration. 2: Redirect - Make all requests redirect to secure HTTPS access. Choose this for new sites, or if you're confident your site works on HTTPS. You can undo this change by editing your web server's configuration. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Select the appropriate number [1-2] then [enter] (press 'c' to cancel): 2
Escribe 2 y pulsa Enter para finalizar la instalación. Deberías ver el siguiente resultado:
Redirecting all traffic on port 80 to ssl in /etc/nginx/conf.d/jellyfin.conf - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Congratulations! You have successfully enabled https://jellyfin.example.com You should test your configuration at: https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html?d=jellyfin.example.com - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - IMPORTANT NOTES: - Congratulations! Your certificate and chain have been saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/jellyfin.example.com/fullchain.pem Your key file has been saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/jellyfin.example.com/privkey.pem Your cert will expire on 2020-10-30. To obtain a new or tweaked version of this certificate in the future, simply run certbot again with the "certonly" option. To non-interactively renew *all* of your certificates, run "certbot renew" - Your account credentials have been saved in your Certbot configuration directory at /etc/letsencrypt. You should make a secure backup of this folder now. This configuration directory will also contain certificates and private keys obtained by Certbot so making regular backups of this folder is ideal. - If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by: Donating to ISRG / Let's Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-le - We were unable to subscribe you the EFF mailing list because your e-mail address appears to be invalid. You can try again later by visiting https://act.eff.org.
Ahora, tu sitio web está protegido con Let’s Encrypt SSL. Puedes acceder a él de forma segura utilizando la URL https://jellyfin.example.com.
Conclusión
Enhorabuena, has instalado con éxito Jellyfin en un servidor Debian 10. Ahora puedes compartir fácilmente tus medios con tus amigos, familiares y otros usuarios.