Cómo instalar WordPress con Nginx y Let’s Encrypt SSL en Ubuntu 22.04
WordPress es un sistema de gestión de contenidos gratuito y de código abierto que se utiliza principalmente para publicar blogs en Internet. Está diseñado para quienes no saben codificar. WordPress facilita la creación y el mantenimiento de sitios web y blogs. Debido a su popularidad, más de un tercio de los sitios web actuales funcionan con WordPress. Está escrito en PHP y utiliza MariaDB y MySQL como base de datos.
En este tutorial, te mostraremos cómo instalar WordPress con Nginx y un certificado SSL gratuito de Let’s Encrypt en Ubuntu 22.04.
Requisitos previos
- Un servidor con Ubuntu 22.04.
- Un nombre de dominio válido apuntado con la IP de tu servidor.
- Una contraseña de root configurada en el servidor.
Instalar Nginx, MariaDB y PHP
Antes de empezar, el servidor LEMP debe estar instalado en tu servidor. Si no está instalado, puedes instalarlo ejecutando el siguiente comando:
apt-get install nginx mariadb-server php php-fpm php-curl php-mysql php-gd php-mbstring php-xml php-imagick php-zip php-xmlrpc -y
Una vez instalado el servidor LEMP, verifica la versión de PHP con el siguiente comando:
php -v
Obtendrás la versión de PHP en la siguiente salida:
PHP 8.1.2 (cli) (built: Apr 7 2022 17:46:26) (NTS)
Copyright (c) The PHP Group
Zend Engine v4.1.2, Copyright (c) Zend Technologies
with Zend OPcache v8.1.2, Copyright (c), by Zend Technologies
A continuación, edita el archivo de configuración de PHP y modifica algunos ajustes por defecto:
nano /etc/php/8.1/fpm/php.ini
Cambia las siguientes líneas:
cgi.fix_pathinfo=0 upload_max_filesize = 128M post_max_size = 128M memory_limit = 512M max_execution_time = 120
Guarda y cierra el archivo cuando hayas terminado.
Crear una base de datos para WordPress
WordPress utiliza una base de datos para almacenar su contenido. Así que tendrás que crear una base de datos y un usuario para WordPress.
En primer lugar, entra en el shell de MariaDB con el siguiente comando:
mysql
Una vez que hayas iniciado la sesión, crea una base de datos y un usuario con el siguiente comando:
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE DATABASE wpdb;
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE USER 'wpuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'securepasssword';
A continuación, concede todos los privilegios a la base de datos de WordPress con el siguiente comando:
MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT ALL ON wpdb.* TO 'wpuser'@'localhost';
A continuación, vacía los privilegios y sal de MariaDB con el siguiente comando:
MariaDB [(none)]> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
MariaDB [(none)]> EXIT;
Una vez que hayas terminado, puedes pasar al siguiente paso.
Instalar WordPress en Ubuntu 22.04
Primero, navega al directorio raíz de la web Nginx y descarga la última versión de WordPress con el siguiente comando:
cd /var/www/html
wget https://wordpress.org/latest.tar.gz
Una vez descargado el WordPress, extrae el archivo descargado con el siguiente comando:
tar -zxvf latest.tar.gz
A continuación, cambia el nombre del archivo de configuración de ejemplo de WordPress.
mv /var/www/html/wordpress/wp-config-sample.php /var/www/html/wordpress/wp-config.php
A continuación, edita el archivo de configuración de WordPress y define la configuración de tu base de datos:
nano /var/www/html/wordpress/wp-config.php
Define la configuración de tu base de datos como se muestra a continuación:
define( 'DB_NAME', 'wpdb' ); /** Database username */ define( 'DB_USER', 'wpuser' ); /** Database password */ define( 'DB_PASSWORD', 'securepasssword' ); /** Database hostname */ define( 'DB_HOST', 'localhost' );
Por razones de seguridad, también tendrás que actualizar las claves de seguridad en tu archivo wp-config. Primero, ve aquí para generarlas. Luego, añádelas como se muestra a continuación:
define('AUTH_KEY', 'Y$I,-gafVeR>Z-8qy&jQ62L}{R)e|lK/#RBh.Y#f+p-P*.8,,hP-iX[q3*tVP-fu');
define('SECURE_AUTH_KEY', 'D)k6o`D G%<()-zXP5{T{v2)Zgo-c+8T-Un=+R3%n/X2=MLDb5$O]UHA%gK| .WR');
define('LOGGED_IN_KEY', 'eL|5#`ul|;MrKm#q$KVl/ky(i}Jc;xrH(Eb|Hwzb/?-.RLSUSX2X[4HD:U:UOP:Y');
define('NONCE_KEY', ']azQ+9f^#~l*r>uPMH5H>ck:?az4o[)*Txo:+MGjE5f&0kag3O9m85g3~VJ6YVWE');
define('AUTH_SALT', 'fAM5&`m4X+{+wSsF.!}-/8@Ce~~u%>}la1bCC,@#+R*t]uYf?[hph/>!Bw>v#oaQ');
define('SECURE_AUTH_SALT', '}|Z&dj_tFV2T$7y(O#O|bwwQ$sH6t!-zdE.MlOHLZ>4WDqG:_Qzn#Allm-UO1#7P');
define('LOGGED_IN_SALT', 'b9Uf~**E_xt@{KWknsAL^9D7Ix3CO.+PpFF~btd)-pG~pXPQ,[c&WRE-NgLG9~)|');
define('NONCE_SALT', '}mTUi&.#i+YJT-TSrbIwqWO<]ut3K%CS~7g.} *NztVlgZDr`?>wxJ+_VW-D_zif');
Guarda y cierra el archivo cuando hayas terminado. A continuación, establece el permiso y la propiedad adecuados para el directorio de WordPress:
chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/wordpress
chmod -R 755 /var/www/html/wordpress
Crear un host virtual Nginx para WordPress
A continuación, tendrás que crear un archivo de configuración del host virtual Nginx para servir a WordPress a través de Internet.
nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/wordpress.conf
Añade la siguiente configuración:
server {
listen 80;
root /var/www/html/wordpress;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
server_name wordpress.example.com;
client_max_body_size 500M;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$args;
}
location = /favicon.ico {
log_not_found off;
access_log off;
}
location ~* \.(js|css|png|jpg|jpeg|gif|ico)$ {
expires max;
log_not_found off;
}
location = /robots.txt {
allow all;
log_not_found off;
access_log off;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php8.1-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
}
Guarda y cierra el archivo y luego verifica la configuración de Nginx con el siguiente comando:
nginx -t
Obtendrás la siguiente salida:
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
A continuación, reinicia los servicios Nginx y PHP-FPM para aplicar los cambios.
systemctl restart nginx
systemctl restart php8.1-fpm
También puedes comprobar el estado de Nginx mediante el siguiente comando:
systemctl status nginx
Obtendrás la siguiente salida:
? nginx.service - A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Thu 2022-05-05 11:36:28 UTC; 10s ago
Docs: man:nginx(8)
Process: 16880 ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/nginx -t -q -g daemon on; master_process on; (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 16882 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nginx -g daemon on; master_process on; (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 16883 (nginx)
Tasks: 3 (limit: 4630)
Memory: 3.4M
CPU: 49ms
CGroup: /system.slice/nginx.service
??16883 "nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx -g daemon on; master_process on;"
??16884 "nginx: worker process" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" ""
??16885 "nginx: worker process" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" ""
May 05 11:36:28 ubuntu2204 systemd[1]: Starting A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server...
May 05 11:36:28 ubuntu2204 systemd[1]: Started A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server.
Instalación web completa de WordPress
Ahora, abre tu navegador web y accede al asistente de instalación de WordPress utilizando la URL http://wordpress.example.com. Serás redirigido a la siguiente página:
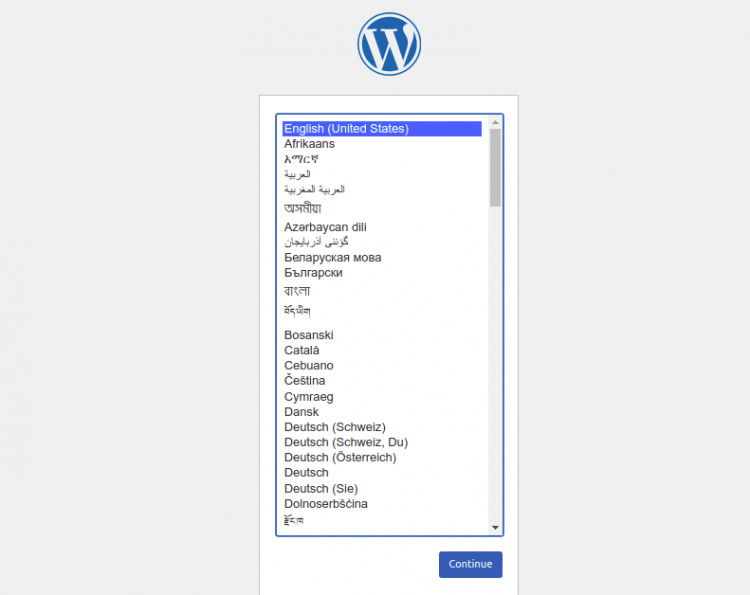
Selecciona tu idioma y haz clic en el botón Continuar. Deberías ver la página de configuración del sitio de WordPress:
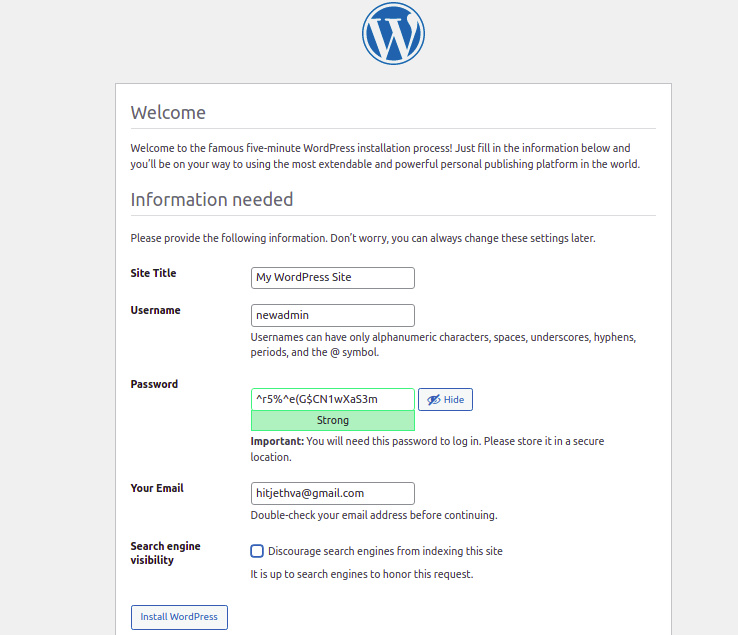
Proporciona el nombre de tu sitio web, el nombre de usuario del administrador, la contraseña y el correo electrónico, y haz clic en el botón Instalar WordPress. Una vez instalado el WordPress, deberías ver la siguiente página:
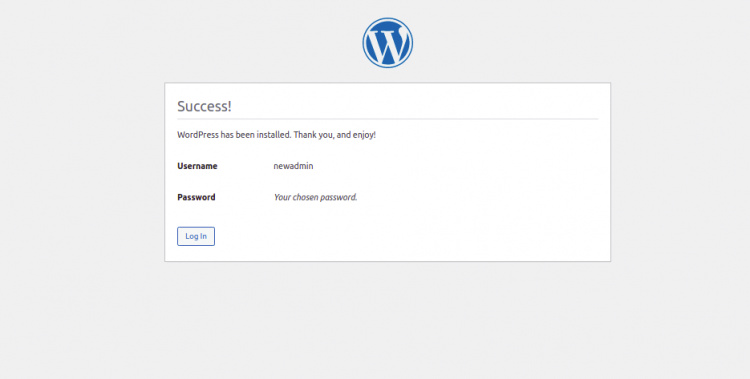
Haz clic en el botón Iniciar sesión. Deberías ver la página de inicio de sesión de WordPress:
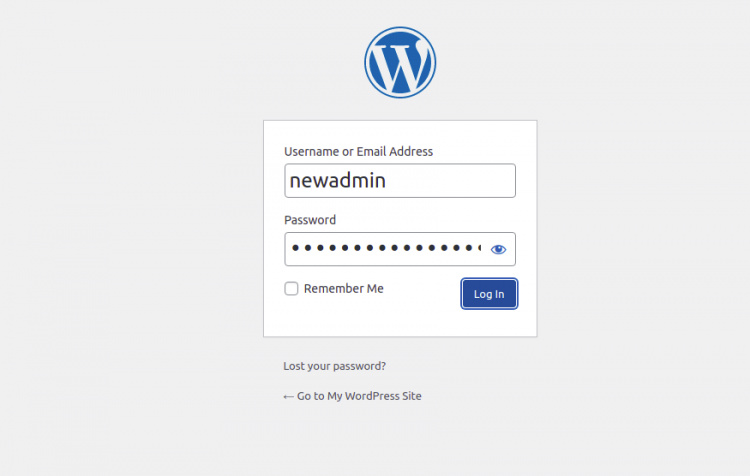
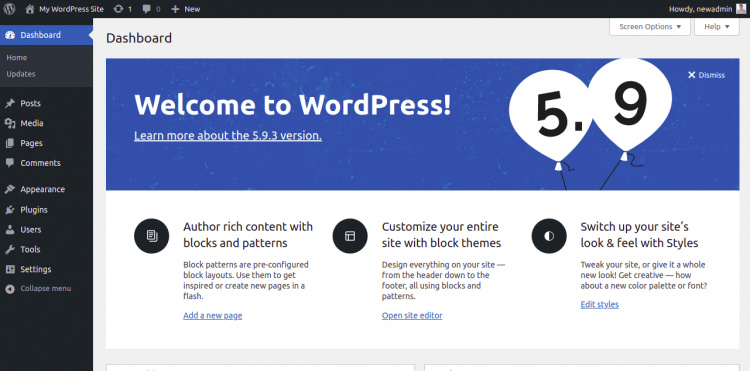
Proporciona tu nombre de usuario y contraseña de administrador, y haz clic en el botón Iniciar sesión. Deberías ver el panel de control de WordPress en la siguiente página:
Habilitar HTTPS en WordPress
Para activar el HTTPS en tu sitio, tendrás que instalar el cliente Let’s Encrypt de Certbot en tu sistema. Puedes instalarlo ejecutando el siguiente comando:
apt-get install python3-certbot-nginx -y
Una vez instalado el cliente Certbot, ejecuta el siguiente comando para habilitar el HTTPS en tu sitio web:
certbot --nginx -d wordpress.example.com
Se te pedirá que proporciones una dirección de correo electrónico válida y que aceptes las condiciones del servicio, como se muestra a continuación:
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log Plugins selected: Authenticator nginx, Installer nginx Enter email address (used for urgent renewal and security notices) (Enter 'c' to cancel): [email protected] - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Please read the Terms of Service at https://letsencrypt.org/documents/LE-SA-v1.2-November-15-2017.pdf. You must agree in order to register with the ACME server at https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (A)gree/(C)ancel: A - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Would you be willing to share your email address with the Electronic Frontier Foundation, a founding partner of the Let's Encrypt project and the non-profit organization that develops Certbot? We'd like to send you email about our work encrypting the web, EFF news, campaigns, and ways to support digital freedom. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (Y)es/(N)o: Y Obtaining a new certificate Performing the following challenges: http-01 challenge for wordpress.example.com Waiting for verification... Cleaning up challenges Deploying Certificate to VirtualHost /etc/nginx/conf.d/wordpress.conf
A continuación, elige si quieres redirigir el tráfico HTTP a HTTPS o no, como se muestra a continuación:
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1: No redirect - Make no further changes to the webserver configuration. 2: Redirect - Make all requests redirect to secure HTTPS access. Choose this for new sites, or if you're confident your site works on HTTPS. You can undo this change by editing your web server's configuration. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Select the appropriate number [1-2] then [enter] (press 'c' to cancel): 2
Escribe 2 y pulsa Intro para finalizar la instalación. Deberías ver la siguiente salida:
Redirecting all traffic on port 80 to ssl in /etc/nginx/conf.d/wordpress.conf - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Congratulations! You have successfully enabled https://wordpress.example.com You should test your configuration at: https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html?d=wordpress.example.com - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - IMPORTANT NOTES: - Congratulations! Your certificate and chain have been saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/wordpress.example.com/fullchain.pem Your key file has been saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/wordpress.example.com/privkey.pem Your cert will expire on 2023-02-08. To obtain a new or tweaked version of this certificate in the future, simply run certbot again with the "certonly" option. To non-interactively renew *all* of your certificates, run "certbot renew" - Your account credentials have been saved in your Certbot configuration directory at /etc/letsencrypt. You should make a secure backup of this folder now. This configuration directory will also contain certificates and private keys obtained by Certbot so making regular backups of this folder is ideal. - If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by: Donating to ISRG / Let's Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-le - We were unable to subscribe you the EFF mailing list because your e-mail address appears to be invalid. You can try again later by visiting https://act.eff.org.
Conclusión
Enhorabuena! has instalado con éxito WordPress con Nginx y Let’s Encrypt SSL en Ubuntu 22.04. Ahora puedes instalar tus temas y plugins preferidos y empezar a crear tu propio sitio web.