Cómo configurar el DNS de ISPConfig sólo en CentOS 7
ISPConfig es un potente panel de control gratuito y de código abierto para servidores Linux que te permite gestionar, supervisar y controlar todas las tareas a través de un navegador web. Es muy seguro, rápido y estable, y lo utilizan muchos administradores de sistemas para gestionar sus servidores. Puedes añadir dominios, direcciones de correo electrónico, sitios web, bases de datos y mucho más con ISPConfig.
Características de ISPConfig
- Soporta tres niveles de acceso: Administrador, Revendedores y Clientes.
- Gestiona múltiples servidores desde un único panel de control.
- Soporta IPv4 e IPv6.
- Compatible con Ubuntu, CentOS, Fedora, Debian y OpenSuSE.
Este tutorial explicará cómo configurar el panel de control ISPConfig en un servidor CentOS 7.
Requisitos
- Un servidor con CentOS 7 instalado.
- Una contraseña de root configurada en tu instancia.
Cómo empezar
Antes de empezar, se recomienda actualizar tu servidor con la última versión. Puedes actualizar el servidor con el siguiente comando:
yum update -y
A continuación, deberás establecer un nombre de host para el servidor. El nombre de host debe ser un nombre de dominio completo. Puedes establecer el nombre de host de tu servidor
hostnamectl set-hostname test.example.com
A continuación, también tendrás que desactivar SELinux en tu servidor. Puedes desactivarlo editando el siguiente archivo:
nano /etc/selinux/config
Cambia las siguientes líneas:
SELINUX=disabled SELINUXTYPE=targeted
Guarda y cierra el archivo. A continuación, reinicia tu sistema para aplicar estos cambios.
Instalar Apache, MariaDB y PHP
Por defecto, la última versión de MariaDB no está disponible en el repositorio por defecto de CentOS. Por lo tanto, tendrás que añadir el repositorio de MariaDB a tu sistema.
Puedes añadirlo con el siguiente comando:
nano /etc/yum.repos.d/MariaDB.repo
Añade las siguientes líneas:
[mariadb] name = MariaDB baseurl = http://yum.mariadb.org/10.4/centos7-amd64 gpgkey=https://yum.mariadb.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB gpgcheck=1
Guarda y cierra el archivo. A continuación, instala el servidor MariaDB con el siguiente comando:
yum install mariadb-server mariadb-client
A continuación, también tendrás que añadir el repositorio Remi para instalar PHP. Puedes añadirlo con el siguiente comando:
yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm yum install yum-utils
A continuación, desactiva PHP5.4 y activa PHP7.2 con el siguiente comando:
yum-config-manager --disable remi-php54 yum-config-manager --enable remi-php72
A continuación, instala PHP con todos los módulos necesarios ejecutando el siguiente comando:
yum install php php-devel php-mysql php-gd php-imap php-ldap php-pear php-xml php-xmlrpc php-pecl-apc php-mbstring php-mcrypt php-snmp php-soap php-tidy curl curl-devel perl-libwww-perl imageMagick libxml2 libxml2-devel mod_fcgid php-cli wget
Una vez finalizada la instalación, abre el archivo php.ini y cambia la configuración de la zona horaria:
nano /etc/php.ini
Cambia la siguiente línea:
date.timezone = Asia/Kolkata
Guarda y cierra el archivo.
A continuación, instala el servidor web Apache con el siguiente comando:
yum install ntp httpd httpd-devel mod_ssl perl-dateTime-format-HTTP perl-dateTime-format-builder
Por último, reinicia el servicio Apache y habilítalo para que se inicie al arrancar con el siguiente comando:
systemctl restart httpd systemctl enable httpd
Instalar y configurar ISPConfig
Primero, descarga la última versión de ISPConfig con el siguiente comando:
wget -O ispconfig.tar.gz https://git.ispconfig.org/ispconfig/ispconfig3/repository/archive.tar.gz?ref=stable-3.1
A continuación, extrae el archivo descargado con el siguiente comando:
tar xfz ispconfig.tar.gz
A continuación, cambia el directorio a ispconfig e inicia la instalación con el siguiente comando:
cd ispconfig3*/install/ php -q install.php
Deberías ver la siguiente pantalla:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
_____ ___________ _____ __ _ ____
|_ _/ ___| ___ \ / __ \ / _(_) /__ \
| | \ `--.| |_/ / | / \/ ___ _ __ | |_ _ __ _ _/ /
| | `--. \ __/ | | / _ \| '_ \| _| |/ _` | |_ |
_| |_/\__/ / | | \__/\ (_) | | | | | | | (_| | ___\ \
\___/\____/\_| \____/\___/|_| |_|_| |_|\__, | \____/
__/ |
|___/
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
>> Initial configuration
Operating System: CentOS 7.6
Following will be a few questions for primary configuration so be careful.
Default values are in [brackets] and can be accepted with .
Tap in "quit" (without the quotes) to stop the installer.
Selecciona el modo experto de instalación y proporciona todas las instrucciones necesarias como se muestra a continuación:
Select language (en,de) [en]: Installation mode (standard,expert) [standard]: expert Full qualified hostname (FQDN) of the server, eg server1.domain.tld [test.example.com]: MySQL server hostname [localhost]: MySQL server port [3306]: MySQL root username [root]: MySQL root password []: admin@123 MySQL database to create [dbispconfig]: MySQL charset [utf8]: The next two questions are about the internal ISPConfig database user and password. It is recommended to accept the defaults which are 'ispconfig' as username and a random password. If you use a different password, use only numbers and chars for the password. ISPConfig mysql database username [ispconfig]: Shall this server join an existing ISPConfig multiserver setup (y,n) [n]: Adding ISPConfig server record to database. Configure Mail (y,n) [y]: [WARN] autodetect for Postgrey failed Force configure Postgrey (y,n) [n]: n Skipping Postgrey Configuring Postfix Generating a 4096 bit RSA private key ...................................................................++ ......................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................++ writing new private key to 'smtpd.key' ----- You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated into your certificate request. What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN. There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank For some fields there will be a default value, If you enter '.', the field will be left blank. ----- Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:IN State or Province Name (full name) []:GUJ Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:JUN Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:IT Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:IT Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:test.example.com Email Address []:[email protected] [WARN] autodetect for Mailman failed Force configure Mailman (y,n) [n]: Skipping Mailman [WARN] autodetect for Dovecot failed Force configure Dovecot (y,n) [n]: n Skipping Dovecot [WARN] autodetect for Courier failed Force configure Courier (y,n) [n]: n Skipping Courier [WARN] autodetect for Spamassassin failed Force configure Spamassassin (y,n) [n]: Skipping Spamassassin [WARN] autodetect for Amavisd failed Force configure Amavisd (y,n) [n]: Skipping Amavisd [WARN] autodetect for Getmail failed Force configure Getmail (y,n) [n]: Skipping Getmail [WARN] autodetect for Jailkit failed Force configure Jailkit (y,n) [n]: Skipping Jailkit [WARN] autodetect for pureftpd failed Force configure pureftpd (y,n) [n]: Skipping pureftpd Configure DNS Server (y,n) [y]: Configuring BIND The Web Server option has to be enabled when you want run a web server or when this node shall host the ISPConfig interface. Configure Web Server (y,n) [y]: Configuring Apache Configuring vlogger [WARN] autodetect for OpenVZ failed Force configure OpenVZ (y,n) [n]: Skipping OpenVZ Configure Firewall Server (y,n) [y]: Configuring Bastille Firewall [WARN] autodetect for Metronome XMPP Server failed Force configure Metronome XMPP Server (y,n) [n]: Skipping Metronome XMPP Server [WARN] autodetect for Fail2ban failed Force configure Fail2ban (y,n) [n]: Skipping Fail2ban Configuring Apps vhost Install ISPConfig Web Interface (y,n) [y]: Installing ISPConfig ISPConfig Port [8080]: Admin password [46bb8280]: admin@123 Re-enter admin password []: admin@123 Do you want a secure (SSL) connection to the ISPConfig web interface (y,n) [y]: Generating RSA private key, 4096 bit long modulus ..............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................++ ............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................++ e is 65537 (0x10001) You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated into your certificate request. What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN. There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank For some fields there will be a default value, If you enter '.', the field will be left blank. ----- Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:IN State or Province Name (full name) []:GUJ Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:JUN Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:IT Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:IT Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:test.example.com Email Address []:[email protected] Please enter the following 'extra' attributes to be sent with your certificate request A challenge password []:admin@123 An optional company name []:IT writing RSA key Configuring DBServer Installing ISPConfig crontab Installing ISPConfig crontab no crontab for root Detect IP addresses Restarting services ... Installation completed.
Una vez hecho esto, puedes pasar al siguiente paso.
Acceder a la Interfaz Web de ISPConfig
ISPConfig ya está instalado y funciona en el puerto 8080. Abre tu navegador web y escribe la URL http://test.example.com:8080. Serás redirigido a la siguiente pantalla:

Ahora, proporciona tu nombre de usuario y contraseña de administrador que has establecido durante la instalación y pulsa el botón Iniciar sesión. Tras iniciar sesión con éxito, deberías ver el panel de control de ISPConfig en la siguiente página:
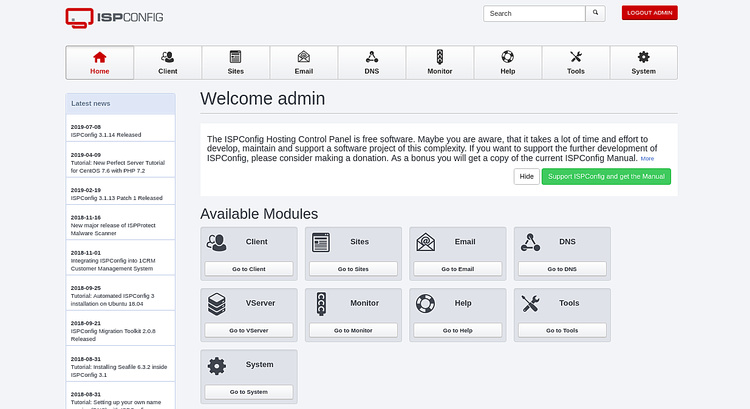
Enhorabuena! has instalado y configurado con éxito ISPConfig DNS solo en CentOS 7. Ahora puedes gestionar fácilmente tus registros DNS desde la interfaz web de ISPConfig. No dudes en preguntarme si tienes alguna duda.