Cómo instalar el gestor de contraseñas autoalojado Passbolt en CentOS 8
Passbolt es un gestor de contraseñas de código abierto que te permite almacenar y compartir tu contraseña de forma segura. Está diseñado para que las pequeñas y medianas organizaciones almacenen y compartan las credenciales de acceso entre los miembros del equipo. Es auto-alojado y está disponible en ediciones comunitarias y de suscripción.
En este tutorial, te mostraremos cómo instalar el gestor de contraseñas Passbolt con Nginx y Let’s Encrypt SSL en CentOS 8.
Requisitos previos
- Un servidor con CentOS 8.
- Un nombre de dominio válido apuntado con la IP de tu servidor.
- Una contraseña de root configurada en tu servidor.
Instalar el servidor LEMP
En primer lugar, instala Nginx y el servidor de bases de datos MariaDB mediante el siguiente comando:
dnf install nginx mariadb-server -y
A continuación, tendrás que instalar la última versión de PHP y otras extensiones PHP necesarias en tu servidor. Por defecto, la última versión de PHP no está disponible en el repositorio por defecto de CentOS. Así que tendrás que añadir los repositorios EPEL y REMI a tu sistema.
Puedes añadir ambos repos con el siguiente comando:
dnf install epel-release -y
dnf install https://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-8.rpm -y
A continuación, desactiva el repo de PHP por defecto y activa el repo de REMI con el siguiente comando:
dnf module reset php
dnf module enable php:remi-7.4
A continuación, instala PHP con otras dependencias necesarias ejecutando el siguiente comando:
dnf install php php-fpm php-intl php-gd php-mysqli php-json php-pear php-devel php-mbstring php-fpm git make unzip -y
Después de instalar todos los paquetes, tendrás que editar el archivo de configuración de PHP-FPM y cambiar el usuario y el grupo a Nginx.
nano /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
Cambia las siguientes líneas:
user = nginx group = nginx
Guarda y cierra el archivo y luego cambia la propiedad del directorio de sesión:
chgrp nginx /var/lib/php/session
A continuación, inicia el servicio de Nginx, MariaDB y PHP-FPM y permite que se inicien al reiniciar el sistema con el siguiente comando:
systemctl start mariadb nginx php-fpm
systemctl enable mariadb nginx php-fpm
A continuación, tendrás que instalar la extensión GNUPG en tu sistema. Puedes instalarla ejecutando los siguientes comandos:
dnf config-manager --set-enabled powertools
dnf install gpgme-devel
pecl install gnupg
echo "extension=gnupg.so" > /etc/php.d/gnupg.ini
A continuación, reinicia el servicio PHP-FPM para aplicar los cambios:
systemctl restart php-fpm
Instalar Composer
Composer es un gestor de dependencias para PHP. Tendrás que instalarlo en tu sistema.
Primero, descarga el archivo de instalación de Composer con el siguiente comando:
php -r "copy('https://getcomposer.org/installer', 'composer-setup.php');"
A continuación, instala Composer con el siguiente comando:
php composer-setup.php --install-dir=/usr/local/bin --filename=composer
Deberías obtener la siguiente salida:
All settings correct for using Composer Downloading... Composer (version 2.0.11) successfully installed to: /usr/local/bin/composer Use it: php /usr/local/bin/composer
A continuación, verifica la versión de Composer con el siguiente comando:
composer -V
Deberías obtener la siguiente salida:
Composer version 2.0.11 2021-02-24 14:57:23
Crear una base de datos
A continuación, tendrás que crear una base de datos y un usuario para Passbolt.
Primero, conéctate a MariaDB con el siguiente comando:
mysql
Una vez conectado, crea una base de datos y un usuario con el siguiente comando:
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE DATABASE passbolt DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT ALL ON passbolt.* TO 'passbolt'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
A continuación, vacía los privilegios y sal de MariaDB con el siguiente comando:
MariaDB [(none)]> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
MariaDB [(none)]> EXIT;
Una vez que hayas terminado, puedes pasar al siguiente paso.
Instalar y configurar Passbolt
En primer lugar, cambia el directorio a la raíz web de Nginx y descarga la última versión de Passbolt con el siguiente comando
cd /var/www
git clone https://github.com/passbolt/passbolt_api.git passbolt
Una vez completada la descarga, cambia el directorio a passbolt e instala todas las dependencias necesarias con el siguiente comando:
cd passbolt
composer install --no-dev
A continuación, tendrás que instalar haveged para generar la clave GPG. Primero, instala el haveged con el siguiente comando:
dnf install haveged
A continuación, inicia el servicio haveged con el siguiente comando:
systemctl start haveged
A continuación, genera la clave GPG con el siguiente comando:
gpg --full-generate-key
Contesta con cuidado a todas las preguntas. Deja el campo de la contraseña en blanco cuando te pidan que establezcas una contraseña:
gpg (GnuPG) 2.2.9; Copyright (C) 2018 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it.
There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.
gpg: directory '/root/.gnupg' created
gpg: keybox '/root/.gnupg/pubring.kbx' created
Please select what kind of key you want:
(1) RSA and RSA (default)
(2) DSA and Elgamal
(3) DSA (sign only)
(4) RSA (sign only)
Your selection?
RSA keys may be between 1024 and 4096 bits long.
What keysize do you want? (2048)
Requested keysize is 2048 bits
Please specify how long the key should be valid.
0 = key does not expire
= key expires in n days
w = key expires in n weeks
m = key expires in n months
y = key expires in n years
Key is valid for? (0)
Key does not expire at all
Is this correct? (y/N) y
GnuPG needs to construct a user ID to identify your key.
Real name: Hitesh
Email address: [email protected]
Comment: Welcome
You selected this USER-ID:
"Hitesh (Welcome) <[email protected]>"
Change (N)ame, (C)omment, (E)mail or (O)kay/(Q)uit? O
We need to generate a lot of random bytes. It is a good idea to perform
some other action (type on the keyboard, move the mouse, utilize the
disks) during the prime generation; this gives the random number
generator a better chance to gain enough entropy.
We need to generate a lot of random bytes. It is a good idea to perform
some other action (type on the keyboard, move the mouse, utilize the
disks) during the prime generation; this gives the random number
generator a better chance to gain enough entropy.
gpg: /root/.gnupg/trustdb.gpg: trustdb created
gpg: key 1A0448FECA43E1F9 marked as ultimately trusted
gpg: directory '/root/.gnupg/openpgp-revocs.d' created
gpg: revocation certificate stored as '/root/.gnupg/openpgp-revocs.d/40733A5076D11E86EF2FE5B51A0448FECA43E1F9.rev'
public and secret key created and signed.
pub rsa2048 2021-03-12 [SC]
40733A5076D11E86EF2FE5B51A0448FECA43E1F9
uid Hitesh (Welcome) <[email protected]>
sub rsa2048 2021-03-12 [E]
Nota: Recuerda la clave secreta generada anteriormente.
A continuación, exporta la clave secreta al archivo serverkey_private.asc y serverkey.asc con el siguiente comando
gpg --armor --export-secret-keys [email protected] > /var/www/passbolt/config/gpg/serverkey_private.asc
gpg --armor --export [email protected] > /var/www/passbolt/config/gpg/serverkey.asc
A continuación, establece la propiedad adecuada al directorio passbolt:
chown -R nginx:nginx /var/www/passbolt
A continuación, inicializa el llavero Nginx con el siguiente comando:
sudo su -s /bin/bash -c "gpg --list-keys" nginx
Salida:
gpg: directory '/var/lib/nginx/.gnupg' created gpg: keybox '/var/lib/nginx/.gnupg/pubring.kbx' created gpg: /var/lib/nginx/.gnupg/trustdb.gpg: trustdb created
A continuación, cambia el nombre del archivo de configuración por defecto de Passbolt:
cp config/passbolt.default.php config/passbolt.php
A continuación, edita el archivo passbolt.php y define la configuración de tu base de datos y la URL base:
nano config/passbolt.php
Cambia las siguientes líneas:
'fullBaseUrl' => 'https://passbolt.linuxbuz.com',
// Database configuration.
'Datasources' => [
'default' => [
'host' => 'localhost',
//'port' => 'non_standard_port_number',
'username' => 'passbolt',
'password' => 'password',
'database' => 'passbolt',
'serverKey' => [
// Server private key fingerprint.
'fingerprint' => '40733A5076D11E86EF2FE5B51A0448FECA43E1F9',
'public' => CONFIG . 'gpg' . DS . 'serverkey.asc',
'private' => CONFIG . 'gpg' . DS . 'serverkey_private.asc',
Guarda y cierra el archivo y luego instala el Passbolt con el siguiente comando:
cd /var/www/passbolt
sudo su -s /bin/bash -c "./bin/cake passbolt install --no-admin" nginx
Deberías obtener el siguiente resultado:
All Done. Took 0.9595s Import the server private key in the keyring --------------------------------------------------------------- Importing /var/www/passbolt/config/gpg/serverkey_private.asc Keyring init OK Passbolt installation success! Enjoy! ?
Configurar Nginx para Passbolt
A continuación, tendrás que crear un archivo de configuración de Nginx para Passbolt. Puedes crearlo con el siguiente comando:
nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/passbolt.conf
Añade las siguientes líneas:
server {
listen 80;
server_name passbolt.linuxbuz.com;
root /var/www/passbolt;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$args;
index index.php;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php-fpm/www.sock;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(.+)$;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param SERVER_NAME $http_host;
}
location ~* \.(jpe?g|woff|woff2|ttf|gif|png|bmp|ico|css|js|json|pdf|zip|htm|html|docx?|xlsx?|pptx?|txt|wav|swf|svg|avi|mp\d)$ {
access_log off;
log_not_found off;
try_files $uri /webroot/$uri /index.php?$args;
}
}
Guarda y cierra el archivo y luego verifica que el Nginx no tenga ningún error de sintaxis:
nginx -t
Salida:
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
A continuación, reinicia el Nginx para aplicar los cambios:
systemctl restart nginx
Asegura Passbolt con Let’s Encrypt SSL
A continuación, tendrás que instalar el cliente Certbot para instalar el SSL de Let’s Encrypt para Passbolt. Puedes instalarlo con el siguiente comando:
dnf install letsencrypt python3-certbot-nginx
A continuación, obtén e instala un certificado SSL para tu dominio lets con el siguiente comando:
certbot --nginx -d passbolt.linuxbuz.com
Se te pedirá que proporciones tu dirección de correo electrónico y que aceptes las condiciones del servicio:
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log Plugins selected: Authenticator nginx, Installer nginx Enter email address (used for urgent renewal and security notices) (Enter 'c' to cancel): [email protected] - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Please read the Terms of Service at https://letsencrypt.org/documents/LE-SA-v1.2-November-15-2017.pdf. You must agree in order to register with the ACME server. Do you agree? - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (Y)es/(N)o: Y - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Would you be willing, once your first certificate is successfully issued, to share your email address with the Electronic Frontier Foundation, a founding partner of the Let's Encrypt project and the non-profit organization that develops Certbot? We'd like to send you email about our work encrypting the web, EFF news, campaigns, and ways to support digital freedom. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (Y)es/(N)o: Y Account registered. Requesting a certificate for passbolt.linuxbuz.com Performing the following challenges: http-01 challenge for passbolt.linuxbuz.com Waiting for verification... Cleaning up challenges Deploying Certificate to VirtualHost /etc/nginx/conf.d/passbolt.conf Redirecting all traffic on port 80 to ssl in /etc/nginx/conf.d/passbolt.conf - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Congratulations! You have successfully enabled https://passbolt.linuxbuz.com - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Subscribe to the EFF mailing list (email: [email protected]). IMPORTANT NOTES: - Congratulations! Your certificate and chain have been saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/passbolt.linuxbuz.com/fullchain.pem Your key file has been saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/passbolt.linuxbuz.com/privkey.pem Your certificate will expire on 2021-06-09. To obtain a new or tweaked version of this certificate in the future, simply run certbot again with the "certonly" option. To non-interactively renew *all* of your certificates, run "certbot renew" - If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by: Donating to ISRG / Let's Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-le
Registrar un usuario para Passbolt
A continuación, deberás registrar un usuario para Passbolt. Puedes hacerlo con el siguiente comando:
cd /var/www/passbolt
sudo su -s /bin/bash -c "./bin/cake passbolt register_user -u [email protected] -f howtoforge -l Demo -r admin" nginx
Deberías obtener la siguiente salida:
____ __ ____
/ __ \____ _____ ____/ /_ ____ / / /_
/ /_/ / __ `/ ___/ ___/ __ \/ __ \/ / __/
/ ____/ /_/ (__ |__ ) /_/ / /_/ / / /
/_/ \__,_/____/____/_.___/\____/_/\__/
Open source password manager for teams
---------------------------------------------------------------
User saved successfully.
To start registration follow the link provided in your mailbox or here:
https://passbolt.linuxbuz.com/setup/install/f81227bc-b0b6-44b5-99a7-6b490a4ba262/5a112de0-6ca4-4e1b-97c8-26453ef3828b
Puedes utilizar el enlace anterior para acceder al Paabolt.
Configurar el cortafuegos
A continuación, tendrás que permitir los puertos 80 y 443 a través del cortafuegos. Puedes hacerlo con el siguiente comando:
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=80/tcp
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=443/tcp
Ahora, recarga el firewalld para aplicar los cambios:
firewall-cmd --reload
Accede a la interfaz web de Passbolt
Ahora, abre tu navegador web y escribe la URL https://passbolt.linuxbuz.com/setup/install/f81227bc-b0b6-44b5-99a7-6b490a4ba262/5a112de0-6ca4-4e1b-97c8-26453ef3828b. Serás redirigido a la siguiente página:
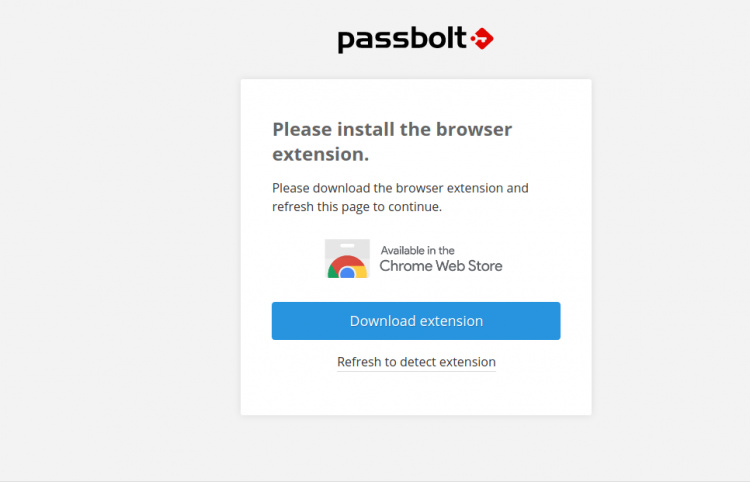
Aquí, tendrás que descargar las extensiones de navegador de Passbolt y actualizar la página una vez instaladas. Deberías ver la siguiente página:
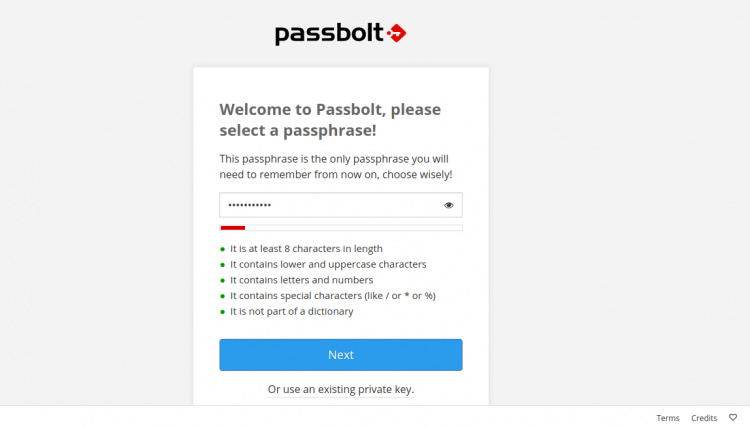
Especifica la contraseña segura y haz clic en el botón Siguiente. Deberías ver la siguiente página:
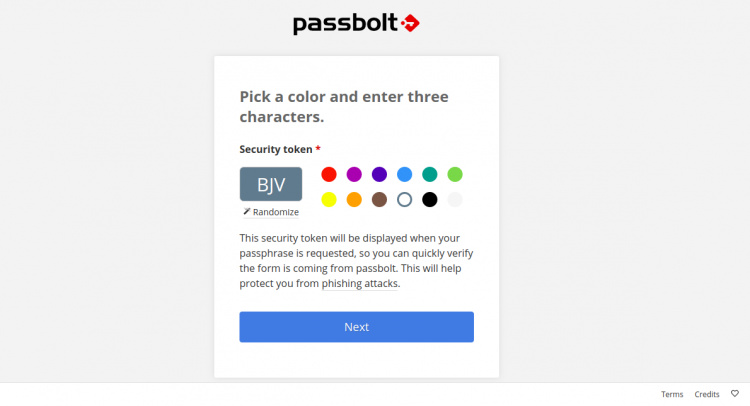
Elige un color, introduce un token de seguridad y haz clic en el botón Siguiente. Serás redirigido al panel de control de Passbolt en la siguiente página:
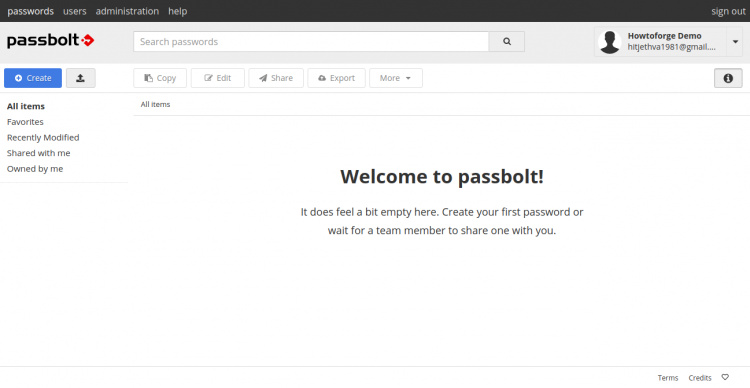
Conclusión
Enhorabuena! has instalado con éxito el gestor de contraseñas Passbolt con Nginx y Let’s Encrypt SSL en CentOS 8. Ahora puedes implementar Passbolt en tu organización y empezar a almacenar y compartir las credenciales de acceso entre los miembros del equipo de forma segura.